21st JUNE 2025 : EDITORIALS SIMPLIFIED
Illegal Migrants: The New National Security Threat in the West
Changing Threat Perception
Western countries now see illegal immigration (people entering a country without permission) as a major national security threat, not countries like Russia or China.
Government ministries for defence and foreign affairs still prepare for war, but the public is more concerned about stopping migrants.
Key Political Issue in the USA
In 1992, James Carville (a U.S. political strategist) said, “It’s the economy, stupid,” highlighting the economy’s importance to voters.
In the 2024 United States presidential election, economy and immigration were both important.
Donald Trump returned to power by focusing on:
High inflation (rising prices of goods and services)
Fear of mass immigration from Mexico
Donald Trump’s Anti-Migrant Stand
Trump claimed 21 million illegal immigrants entered the United States under President Joseph Biden (though likely incorrect).
His campaign mixed:
Economic fears (job loss and foreign trade)
Cultural fears (loss of American identity)
This gained huge support from conservative (right-wing) voters.
Events in California
Donald Trump’s government started mass arrests and deportations (forcing migrants to leave the country).
Latino communities protested and clashed with police.
Trump sent United States military troops and the National Guard to stop what he called “rebellion.”
Gavin Newsom, Governor of California, called this a violation of State rights and human rights.
Europe’s Immigration Crisis
Europe saw a mass inflow of refugees due to:
Wars in Syria and Iraq
Poverty and collapse in African countries
Right-wing politicians in Europe demanded emergency actions.
Even when not winning elections, they made anti-immigrant views popular.
Many traditional parties started copying these views.
Record Number of Migrants
The term "migrant" has become controversial.
In 2020, there were 281 million international migrants, up from 153 million in 1990.
The International Organization for Migration (IOM) provided this data.
Anti-Immigrant Views in the Global South
Not just Western countries—Brazil, Turkey, South Africa, Indonesia, and India also have rising anti-immigrant feelings.
Citizens worry foreigners take jobs and limited resources.
India’s Illegal Immigration Issue
Estimated 20+ million illegal immigrants from Bangladesh entered India through the eastern border.
Concerns include:
Demographic change (change in population structure)
Creation of exclusive areas (enclaves) that may support Islamist extremism
Right-wing parties talk about an invasion, like Donald Trump.
Secular parties oppose this view and support migrants’ rights.
Economic Importance of Migrants
Migrants help host countries (countries they move to) by:
Filling labour shortages
Supporting economies with declining birth rates
Economists say legal migration helps long-term economic growth.
Politics vs. Reality
Politicians blur the difference between:
Legal and illegal migrants
Refugees escaping war and migrants seeking better jobs
Though solutions exist to match migrants with job markets, politics prevents implementation.
The global immigration crisis is likely to get worse, irrational, and violent.
Emergency and Indian Cinema: Reel Life under Real Oppression (1975–1977)
Relevance:
For Class 10 Social Science (Civics), the topic relates to understanding democracy, suppression of civil rights, and censorship in media.
For Class 11 Political Science, it explains concepts like electoral autocracy and how democracy can be weakened through Emergency powers.
For Class 11 History (Themes in Indian History), it gives insight into political developments in India after independence, especially during the 1970s.
For Class 12 Political Science (Contemporary World Politics & Politics in India Since Independence), this is a direct reference to the 1975 Emergency, with examples of political repression, media control, and challenges to democratic values.
For Class 12 Sociology, the topic is relevant to discussions on media, state power, resistance movements, and how civil rights are affected under authoritarian rule.
For Class 12 English (Flamingo/Vistas), it provides useful content for comprehension and writing practice, especially on themes like freedom of expression, democracy, and individual rights.
What Was the Emergency?
Period: June 25, 1975 – March 21, 1977
Declared by Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, citing internal disturbances.
India became a democratic despotism (dictatorship under democracy) and electoral autocracy (elections continued but freedom curtailed).
Mass media, including films, were censored, and artistic freedom was restricted.
White Paper on Media Misuse
Published in August 1977 by the Janata Party government.
Documented how the government misused media, including cinema, during the Emergency.
Censorship in South Indian Films
1. Kabani Nadi Chuvannappol (When the Kabani River Turned Red, 1975) – Malayalam
Director: P.A. Backer
Producer: Pavithran
Actor: T.V. Chandran (debut)
Plot: Student rebellion against authority
Events:
Shot in Bengaluru to avail ₹50,000 subsidy by Karnataka Government.
Harassed during shooting; 1,000 feet cut by censors.
Later passed, but was withdrawn by police in Thiruvananthapuram, further edits ordered.
2. Chanda Maruta (Rogue Winds, 1975) – Kannada
Director: Pattabhi Rama Reddy
Actor: Snehalatha Reddy
Plot: Predicted political unrest; inspired by P. Lankesh’s play
Events:
Banned by censors.
Snehalatha Reddy was arrested, tortured, died while on parole in 1977, aged 45.
MT Vasudevan Nair planned a film (not made).
Her story is documented in Prison Diaries (2019) by Uma Chakravarti.
Also featured in Prisoners of Conscience (1978) by Anand Patwardhan.
Censorship in Hindi Films
Aandhi (Storm, 1975)
Director: Gulzar
Actors: Sanjeev Kumar, Suchitra Sen
Thought to resemble Indira Gandhi.
Passed only after revisions.
Kissa Kursi Ka (1975)
Director: Amrit Nahata
Type: Political satire
Banned, all prints and negatives destroyed.
Andolan (1975)
Director: Lekh Tandon
About 1942 Quit India Movement
Not released, as it contained underground resistance content.
Sholay (1975)
Huge hit but censors forced a change in ending scenes.
Artists Targeted
Kishore Kumar
Playback singer
Refused to perform for government event.
Punishment:
Banned from All India Radio and Doordarshan
Record sales banned
Dev Anand
Actor and filmmaker who opposed Emergency publicly.
Called it a “dark night”, “nightmare”, and “insult to the people”.
Started National Party of India, but it was disbanded after Emergency ended in 1977 due to lack of support.
Conclusion
The Emergency severely affected the freedom of cinema and artists.
Despite oppression, some stood up and resisted.
As India marks 50 years since Emergency, these stories must be remembered.
Quantum Challenge – Why India Needs Administrative Reform
Relevance:
Class 10
Science: Supports understanding of future technologies like quantum communication and cybersecurity.
Information Technology: Real-life application of secure data transmission.
Current Affairs/General Awareness: Helpful for project work or internal assessments.
Class 11
Physics: Related to topics in modern physics, quantum mechanics, and wave theory.
Political Science: Shows impact of science policy and government funding on national development.
Economics: Connects with budgeting, resource allocation, and the role of innovation.
Class 12
Computer Science: Real-world case of data security and encryption.
Political Science (Contemporary World Politics): Explores how technology shapes power dynamics.
Business Studies: Illustrates start-up environment, venture capital challenges, and administrative barriers.
Geography: Relevance in space communication and satellite networks.
What Happened Recently?
Scientists from IIT-Delhi and DRDO made a big step in quantum cybersecurity.
They showed how two people or stations 1 km apart can send secret messages using quantum key distribution.
If someone tries to hack or listen in, the system instantly detects it by changing the keys.
If this is expanded to satellites, then secure communication could happen across India without fear of spying.
Why Is This Important?
Today’s messages are kept safe using hard math problems.
But quantum computers in the future might break those protections.
So, we need new security that even powerful computers can’t crack — that’s what quantum cybersecurity offers.
National Quantum Mission
India launched the National Quantum Mission in 2023.
Budget: ₹6,003 crore till 2031.
Focus: 4 areas, one of which is quantum communication (like this project).
Problems in the Mission
Very little money has been actually given so far.
Startups are getting almost no private investment.
Scientists face many problems:
Late funding
Too much paperwork
No single-point approval system
India depends on other countries for:
Hardware like cryostats and sensors
Software made by foreign companies
Government pay is low, so scientists often:
Work on short-term contracts
Have to rent equipment
India vs. World
India’s current spending (₹6,003 crore) is less than what was planned earlier (₹8,000 crore).
Other countries spend much more:
USA: 5 times more
China: 20 times more
What Needs to Be Done
India cannot grow in quantum science if it continues with old systems.
We can’t just add money and scientists — we need to change how the system works.
Administrative reforms are urgently needed to make full use of scientific talent and new technologies.
It is still not too late for India’s voice to be heard
Relevance
Class 11
Political Science (Indian Constitution and Politics): India's role in international diplomacy.
Geography: Regional conflicts in West Asia and their global impact.
History: Relevance of international peace efforts and UN role.
Political Science (Indian Constitution and Politics): India's role in international diplomacy.
Geography: Regional conflicts in West Asia and their global impact.
History: Relevance of international peace efforts and UN role.
Class 12
Political Science (Contemporary World Politics): Role of global powers, international conflict, diplomacy.
Economics: Impact of sanctions and wars on trade and connectivity.
Business Studies: Role of geopolitical stability for global business routes.
Geography: Chabahar Port, strategic corridors, India’s trade links to Central Asia.
Political Science (Contemporary World Politics): Role of global powers, international conflict, diplomacy.
Economics: Impact of sanctions and wars on trade and connectivity.
Business Studies: Role of geopolitical stability for global business routes.
Geography: Chabahar Port, strategic corridors, India’s trade links to Central Asia.
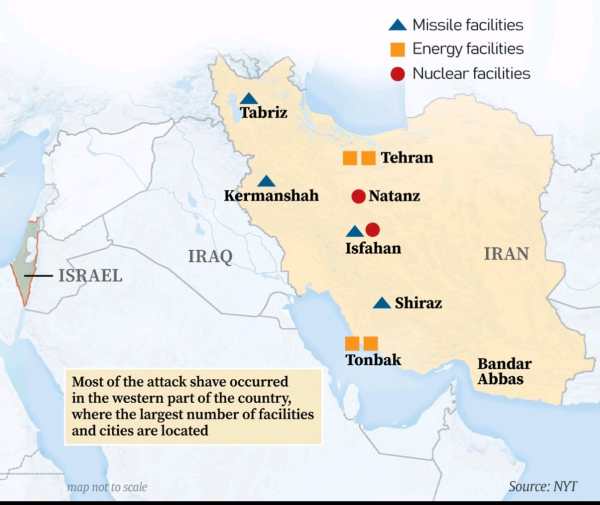
Israel's Attack on Iran (June 13, 2025)
Israel carried out an unlawful military strike inside Iran.
The Indian National Congress strongly condemned this act.
The strike could cause serious regional and global instability.
This came during promising peace talks between Iran and the United States (US).
Iran's Nuclear Program Status
In March 2025, US Director of National Intelligence, Tulsi Gabbard, confirmed:
Iran is not making nuclear weapons.
Iran’s Supreme Leader, Ali Khamenei, has not approved any nuclear arms program since it was halted in 2003.
Israel’s Leadership and Actions
Under Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu:
Israel has expanded illegal settlements.
Partnered with ultra-nationalist groups.
Opposed the two-state solution (peace between Israel and Palestine).
Netanyahu’s leadership is linked to violence and extremism.
Was accused of encouraging hate before Prime Minister Yitzhak Rabin was assassinated in 1995.
US Role Under President Donald Trump
Trump previously opposed endless wars, but now backs military action.
On June 17, 2025, Trump ignored US intelligence and wrongly claimed Iran is "very close" to nuclear weapons.
Double Standards
Israel has nuclear weapons but criticizes Iran for possible nuclear ambitions.
Iran signed the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT).
In 2015, Iran agreed to reduce its nuclear activity under the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA).
The US left this deal in 2018, harming regional peace.
India’s Strategic Interests and Diplomatic Position
India suffered due to sanctions on Iran:
Delays in projects like Chabahar Port and International North-South Transport Corridor.
Iran helped India at the United Nations (UN) during Kashmir crisis in 1994.
Past governments in Iran (before 1979) supported Pakistan in wars with India.
India's Relations with Both Sides
India has strong ties with both Iran and Israel.
This gives India a special role to promote peace in West Asia.
Many Indians live and work in the region, making peace a national interest.
India’s Silence on Gaza and Iran
Over 55,000 Palestinians have died in Israel’s Gaza attacks.
India’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) government is silent, breaking tradition of moral diplomacy.
India should speak for a two-state solution: independent Palestine and Israel living in peace.
Final Message
India must:
Speak clearly
Act diplomatically
Help reduce violence and return to peace talks.
It is still not too late to act.
U.K.–India Cultural Partnership
Relevance:
Class 10
English: Speech, essay, report topics.
Social Science: Trade, diplomacy, cultural diversity.
English: Speech, essay, report topics.
Social Science: Trade, diplomacy, cultural diversity.
Class 11
Political Science: Role of culture in diplomacy.
Fine Arts: Career and scope in creative industries.
Political Science: Role of culture in diplomacy.
Fine Arts: Career and scope in creative industries.
Class 12
Economics: Creative industry’s role in GDP and jobs.
Business Studies: Public-private partnerships, case study of Royal Enfield.
History: Indo-British cultural heritage.
Economics: Creative industry’s role in GDP and jobs.
Business Studies: Public-private partnerships, case study of Royal Enfield.
History: Indo-British cultural heritage.
Key Events
In May 2025, India and the U.K. signed a Free Trade Agreement.
A new cultural deal called Programme of Cultural Cooperation (POCC) was also signed.
Signed by Lisa Nandy (U.K.) and Gajendra Singh Shekhawat (India).
What is POCC?
The agreement will help both countries work together in five cultural areas:
Digital technologies in culture
Exhibitions and collections
Events and performances
Cultural heritage protection
Sustainability
Growth of Creative Industries
The creative economy is growing fast and may reach 10% of global GDP by 2030.
It creates many jobs and supports economic growth.
India hosted the WAVES summit for the first time in 2025.
Institutions Involved
British Council, Arts Council England, British Library, British Museum, and others.
India and U.K. aim to share art, knowledge, and digital experiences.
Why This Matters for India
India has a $35 billion creative economy with 8% of the workforce in it.
Strong presence in non-metro regions like Badgam and Tiruppur.
Over 300 universities and 3,000 colleges offer design and art courses.
Challenges and Opportunities
Need more education, training, and global cooperation.
New technologies like AI, AR, and VR are changing the creative industry.
Report recommends teaching tech skills in creative fields.
Business Example
Royal Enfield, with UNESCO, helps preserve cultural heritage in the Himalayas.
Supports over 580 artisans through sustainable textile projects.
People Are the Bridge
Festivals like Hornbill and events like Wales in India show deep people-to-people ties.
Culture builds peace, understanding, and shared progress.
Government Panel on Coaching Dependency and Exams
Purpose of the Panel
Formed by the Union Education Ministry.
Aims to:
Reduce students' dependence on coaching centres.
Review the fairness and effectiveness of competitive exams.
Formed by the Union Education Ministry.
Aims to:
Reduce students' dependence on coaching centres.
Review the fairness and effectiveness of competitive exams.
Panel Members
Head: Vineet Joshi, Higher Education Secretary.
Includes:
CBSE Chairman.
Joint Secretaries from School and Higher Education Departments.
Representatives from IIT-Madras, NIT-Trichy, IIT-Kanpur, and NCERT.
Principals from Kendriya Vidyalaya, Navodaya Vidyalaya, and a private school.
Head: Vineet Joshi, Higher Education Secretary.
Includes:
CBSE Chairman.
Joint Secretaries from School and Higher Education Departments.
Representatives from IIT-Madras, NIT-Trichy, IIT-Kanpur, and NCERT.
Principals from Kendriya Vidyalaya, Navodaya Vidyalaya, and a private school.
Key Focus Areas
1. Coaching Dependency
Study why students rely on coaching.
Identify gaps in school teaching such as:
Lack of critical thinking
Focus on rote learning
Weak reasoning and analytical skills
Study why students rely on coaching.
Identify gaps in school teaching such as:
Lack of critical thinking
Focus on rote learning
Weak reasoning and analytical skills
2. Dummy Schools
Examine the role of dummy schools that:
Enroll students only on paper.
Let them focus entirely on coaching.
Examine the role of dummy schools that:
Enroll students only on paper.
Let them focus entirely on coaching.
3. Assessments and Exams
Review how school and college exams prepare students for entrances.
Study the lack of formative assessments and its impact.
Review how school and college exams prepare students for entrances.
Study the lack of formative assessments and its impact.
4. Limited Seats & Career Awareness
Analyze how few seats in top colleges push students to coaching.
Check how aware students and parents are about career options.
Assess the role of career counselling in schools.
Analyze how few seats in top colleges push students to coaching.
Check how aware students and parents are about career options.
Assess the role of career counselling in schools.
5. Coaching Centre Practices
Review advertising methods used by coaching centres.
Curb misleading claims and highlight fair practices.
Review advertising methods used by coaching centres.
Curb misleading claims and highlight fair practices.








No comments:
Post a Comment